Marketplace
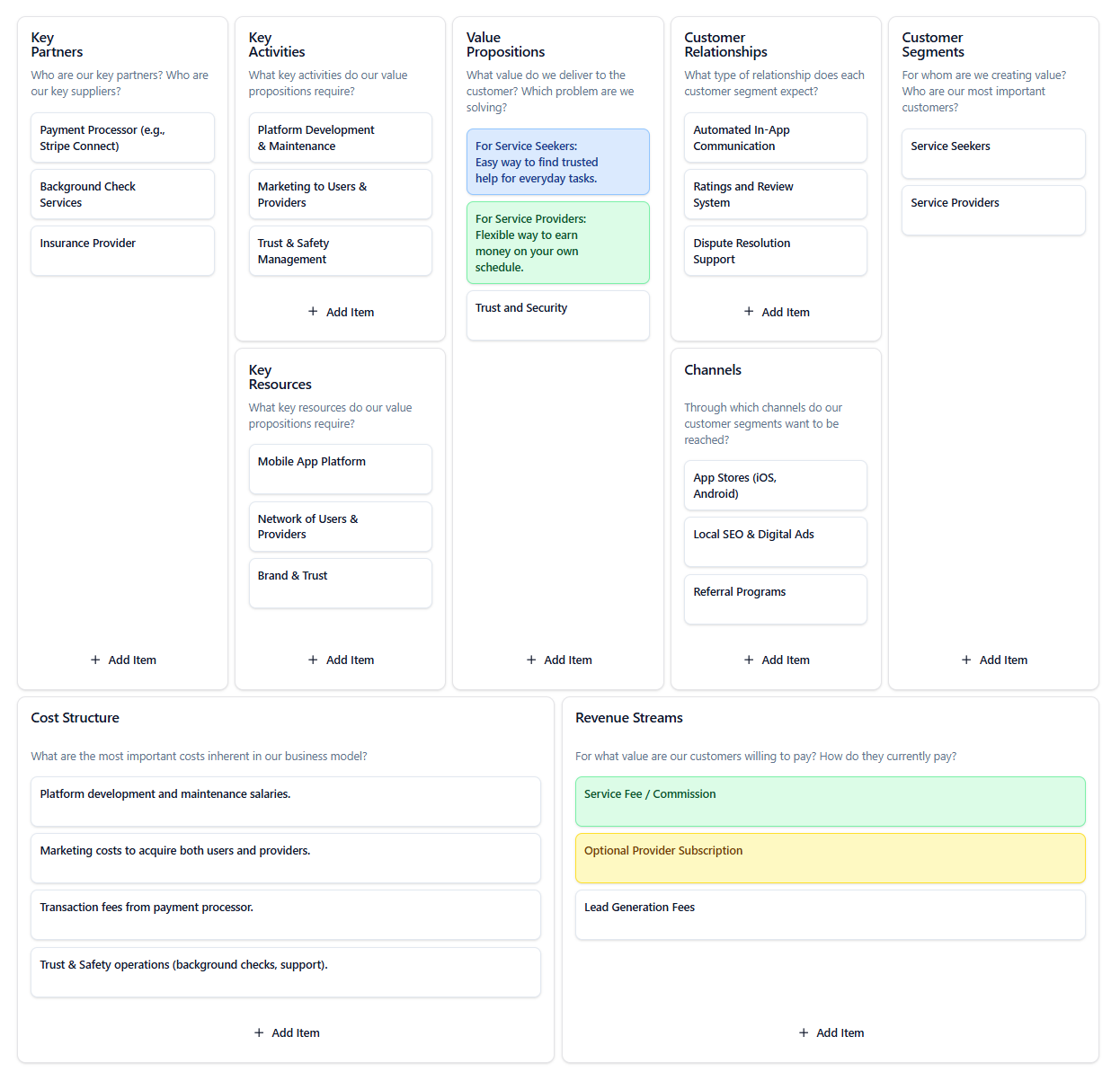
Peer-to-Peer Local Services Marketplace
An app connecting people who need tasks done (e.g., cleaning, handyman work) with trusted local providers.
Analysis & Interpretation
Background
This Peer-to-Peer Marketplace addresses a two-sided market: connecting individuals who need tasks done with those who can provide the service. The model’s success hinges on its ability to build trust and efficiently match supply with demand. This analysis focuses on the critical role of network effects and trust mechanisms.
Key Strategic Insights
- Two-Sided Value Proposition is Key: The model correctly identifies distinct value propositions for ‘Service Seekers’ (convenience) and ‘Service Providers’ (flexible income). All key activities must serve both sides of this market.
- Trust is the Product: ‘Key Activities’ like ‘Trust & Safety Management’ and ‘Key Partners’ like ‘Background Check Services’ are not operational details; they are fundamental to the ‘Trust and Security’ value proposition. Without them, the marketplace fails.
- Network Effects as the Unfair Advantage: The most critical ‘Key Resource’ is the ‘Network of Users & Providers’. The business model must prioritize ‘Key Activities’ (Marketing to both sides) and ‘Channels’ (Referral Programs) that accelerate this network effect to create a defensible moat.
Strategic Summary
This is a classic marketplace model where solving the ‘chicken and egg’ problem is paramount. The initial strategy must be hyper-focused on a specific geographic area or service category to build liquidity. The key investment should be in technology and operations that build and maintain trust, as this is the platform’s most valuable asset and the foundation for future growth.
How It Was Built
This canvas demonstrates how the platform’s AI and visualization tools can help structure and refine a complete business strategy.

Smart Idea Generation
With AI Brainstorm, initial ideas were developed for the Value Proposition and Customer Segments, setting a clear strategic foundation.

Visual Structuring
Distinct colors separated cost and revenue sections, while tags linked related activities to maintain logical organization.

Data-Driven Insights
After the canvas was completed, the AI Insight Tool highlighted Key Partners as a vital element to strengthen for sustainable growth.
Try It Yourself
Experience the process hands-on by loading this canvas into the tool. Experiment with AI suggestions, adjust the layout, and watch how each change reshapes your strategy in real time.
